- +86 13512168749
- oversea@zlmcu.com
- Buy Online


When using the TCP/IP module of ZLSN2000,users often ask how to handle multiple IP, namely, multiple computers/network devices want to do TCP/IP communication with ZLSN2000. This article introduces various methods of this multi-IP communication.
In some applications, a single ZLAN TCP/IP module needs to communicate with multiple computer/network devices, that is, multiple IP communications. For such demand, here are a few kinds: UDP broadcast mode, UDP multicast mode, UDP dynamic destination mode, TCP Server mode, TCP Client multi-destination IP, UDP multi-destination IP, serial ports modification way.
Among them, UDP dynamic destination mode and serial port modification are only applicable to time-share multi-IP communication. Other modes support simultaneous and multi-purpose IP communication. Among them, UDP broadcast mode and UDP multicast mode adopt broadcasting and multicast mode, and the transmission speed is faster than other methods in the target IP. Multi-IP communication in TCP server mode is one of the most widely used methods. If there is no working mode, you can choose this way. TCP Client multi-destination IP, UDP multi-destination IP needs to use ZLSN2000MDIP module, which is a class of customized modules, different from ZLSN2000.
In the same physical subnet of LAN mode, UDP broadcasting is an easy way to provide multi-machine communication. When using this method, only the ZLSN2000 TCP/IP module is set to the UDP working mode, and the destination IP is 255.255.255.255, and the port is the port of the destination computer. The advantage of UDP broadcast mode is that it sends data fast and covers a wide range of destination IP. This is because the ZLSN2000 module only needs to send a packet, rather than sending one data per IP, so that all IP can receive data.
Disadvantages of UDP broadcast mode: (1) poor confidentiality. This method will send data to IP that does not need data. (2) increasing the network burden, and the increase of broadcasting in the LAN will affect the overall data flux of the network and increase the network load.
ZLSN2000TCP/IP module supports UDP multicast. UDP multicast has the advantages of UDP broadcasting, and UDP multicast mode partially solves the problem of UDP broadcast. Only the computers that join the IP group can receive data, and the multicast data does not significantly increase the network load. Multicast data can also be extended across the router to the external network. However, it still cannot prevent the arbitrary addition into IP groups, so that confidentiality is not guaranteed.
UDP dynamic destination mode is to configure ZLSN2000 to communicate with multiple IP. But this configuration is time-sharing multi-IP communication.
The new version of the ZLSN2000 module (also known as ZLSN2003) supports simultaneous and 100 IP communications in the TCP server mode, and 100 computers can be connected to a ZLSN module at the same time. This mode is recommended if the user's computer/device can connect to ZLSN as a TCP client.
The ZLSN2000-MDIP core module and its derivatives support multiple destination IP, which is to initiate a connection to multiple destination IP and port when the module works in the TCP client mode. After the connection is complete, you can communicate with the server of multiple destination IP. The completion of multi-destination IP is shown in the figure.
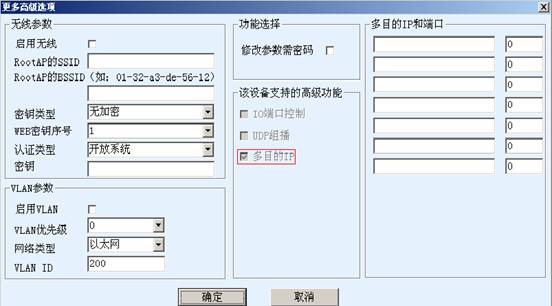
Similar to TCP client multi-destination IP, ZLSN2000MDIP also supports sending data to multiple IP in UDP mode. The setup method is basically the same as the TCP client multi-destination IP, except now that the working mode is UDP.
ZLAN ZLSN2000TCP/IP module provides a flexible serial port modification working mode of function, which makes that if the user use a MCU controller (or computer serial port software) to connect with serial port of ZLSN2000, it can flexibly control the ZLSN2000 in any mode of TCP server, the TCP client and the UDP, the data sent to the destination IP and port can be set at any time. If you use a serial command to modify the destination IP and port, the flexibility is very good, and the number of destination IP is unlimited. However, this pattern is also multi-IP communication.
