- +86 13512168749
- oversea@zlmcu.com
- Buy Online


SNMP is short for Simple Network Management Protocol. The SNMP protocol has been adopted by most network devices due to its good scalability and ease of use. Through the SNMP protocol, you can view the operating parameters and setting parameters of the serial device server. More importantly, these functions can be integrated into the same NMS system of the user, and no additional vendor-supplied software tools are needed, facilitate the management of network devices.
The serial port server/serial to Ethernet module provided by ZLAN with the suffix -SNMP (for example, ZLSN2002-SNMP) supports the SNMP agent function. The network management system (NMS) on the computer can obtain all the current parameters of the network module through the SNMP protocol, and can set all the parameters at the same time.
Use ZLVircom tool to check whether the device supports SNMP function: To view the device is "Device Manage" -> " Edit Device" -> "More advanced setting...", open the advanced options dialog box, see the advanced features supported by the device:

If the snmp is ticked on the left, then the snmp function is supported
ZLAN provides the MIB repository file ZLAN_MIB.mib in the standard ASN.1 syntax format. When used, this information base is imported into the user's NMS management system, and the ZLAN device can be managed. The following figure shows the situation after a network management system imports ZLAN MIB.
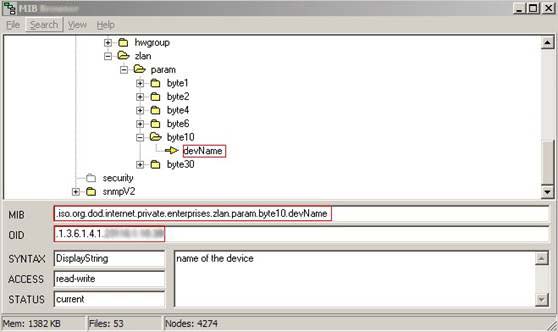
ZLAN_MIB exists under .iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprises. It will add zlan nodes below this node and generate param nodes under zlan. Each node parameter below has its own OID number.
After importing the ZLAN MIB to the user's NMS system, you can obtain the parameters and set parameters by sending SNMP “get” and “set” commands to the IP address on which the ZLSN module resides. It includes the status of whether the current serial-to-Ethernet module establishes a TCP connection and so on.
